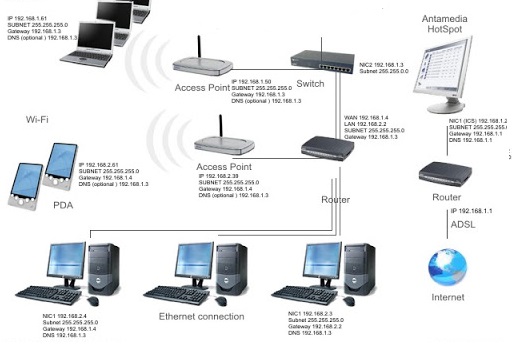
A computer network or data network is a telecommunications network which allows computers to exchange data. In computer networks, networked computing devices exchange data with each other using a data link. The connections between nodes are established using either cable media or wireless media.
Data networks can be categorized and labeled according to the geographical area that the network covers. The four geographically defined networks: a Local Area Network (LAN), a Campus Area Network (CAN), a Metropolitan Area Network (MAN), and a Wide Area Network (WAN).
An excellent example of a network is the Internet, which connects millions of people all over the world.
Switches, routers, and wireless access points are the essential networking basics. Through them, devices connected to your network can communicate with one another and with other networks, like the Internet. Switches, routers, and wireless access points perform very different functions in a network.
The Open System Interconnection (OSI) model defines a networking framework to implement protocols in seven layers.
The 7 Layers of the OSI:
- Layer 7 – Application.
- Layer 6 – Presentation.
- Layer 5 – Session.
- Layer 4 – Transport.
- Layer 3 – Network.
- Layer 2 – Data Link.
- Layer 1 – Physical.